Commercial TVs and other displays went a long way for the last 80 years. Being originally bulky devices occupying a large space in living rooms, nowadays they became flat panels that can be easily mounted on the wall. This led to a mounts’ standardization problem. Each manufacturer tried to create a unique mounting method which caused chaos on the market. Everything changed when VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association) has developed a unified standard (know colloquially as VESA) which is used to this day.
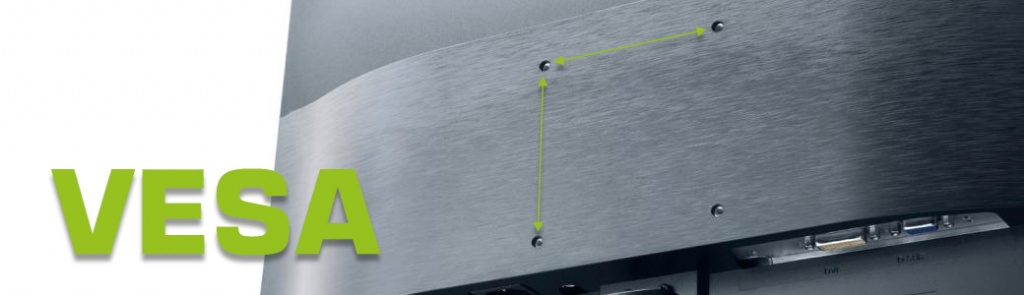
The vast majority of retailers and manufacturers specify VESA in data sheets. However, you may find yourself in a situation when this parameter is absent. In such cases you can define the necessary VESA parameters with the help of a simple ruler. Unclear numbers 50x50 and 75x75 are in fact the distance between mounting holes. The first number means vertical distance and the second one means horizontal.
Also, the standardization made it easy to learn necessary VESA on basis of monitor’s diagonal. For example, 22’’ screens usually utilize 75x75 VESA. In case of 32’’ and larger screens VESA 200x200 is used. To put it simply – the larger the screen, the larger the VESA.
|
Diagonal |
Max weight |
VESA |
|
4’’-7’’ |
2 kg |
100x50 |
|
8’’-11’’ |
4,5 kg |
75x35 |
|
12’’-22’’ |
8 kg |
75x50, 75x75 |
|
12’’-22’’ |
14 kg |
100х50, 100х100 |
|
23’’-30’’ |
22,7 kg |
200х100, 200х50 |
|
31’’-90’’ |
113,6 kg |
200х200 and more |
It is also important to always double-check the VESA because sometime you may meet nonstandard mounting parameters. Such cases are really rare and usually met in TV’s manufactured pre 1998, but better safe than sorry. Always pay attention to VESA parameter and you will be able to create a perfect workplace with ease.
